How Consumers Are Driving Change in Food Packaging
In the evolving landscape of food packaging, consumer demand for sustainability is a significant catalyst for change. Increasingly informed about environmental impacts, consumers are favouring products with reduced packaging waste and recyclable materials.
This shift is compelling companies to innovate, developing eco-friendly packaging solutions that meet these expectations. As businesses adapt to these demands, they not only address environmental concerns but also build brand loyalty.
The relationship between consumer preferences and corporate practices is transforming the industry, prompting questions about how far these changes can go and what innovations lie ahead.
The Role of Consumer Demand in Sustainable Packaging
Consumer demand serves as a pivotal catalyst in the transition towards sustainable food packaging solutions. As awareness of environmental concerns grows, consumers increasingly prioritise packaging that minimises ecological impact.
This shift in consumer preferences is compelling companies to rethink traditional packaging methods and invest in sustainable alternatives. According to a YourView poll of 692 South African consumers, 34% indicated that sustainability and eco-friendliness are paramount in their packaging choices.
This heightened consumer awareness has led to significant changes in the industry. Companies are now more inclined to explore environmentally responsible packaging to meet consumer expectations. The demand for sustainable packaging is not just a passing trend but a growing movement that impacts purchasing decisions and brand loyalty.
Consumers’ willingness to support brands that adopt eco-friendly practices drives market competition, prompting companies to innovate and differentiate themselves through sustainable packaging. This consumer-driven pressure is crucial for the industry’s shift towards reducing plastic waste, adopting biodegradable materials, and enhancing recyclability.
As a result, consumer demand plays an essential role in fostering a more sustainable future, influencing companies to adopt practices that align with ecological preservation and sustainability goals.
unnamed
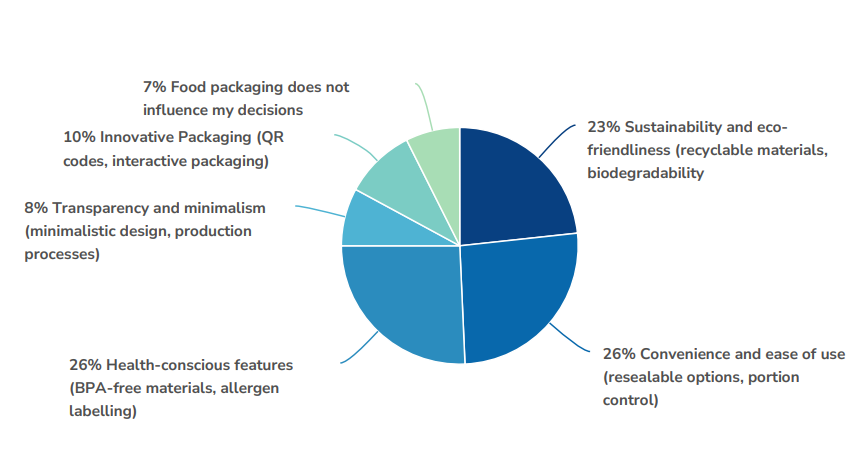
Respondents from the YourView panel stated the below are leading factors that influence their food packaging choices:
- 8% Transparency and minimalism (minimalist design, production processes)
- 10% Innovative Packaging (QR codes, interactive packaging)
- 23% Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness (recyclable materials, biodegradability)
- 26% Health-conscious features (BPA- free materials, allergen labelling)
- 26% Convenience and ease of use (resealable options, portion control).
Biodegradable and Compostable Materials
Innovations in biodegradable and compostable materials are revolutionising the food packaging industry by offering sustainable alternatives that minimise environmental impact. As consumer awareness about environmental issues grows with an astonishing 23.3% of total consumers from a YourView survey , show an increased demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions is driving significant advancements in this sector. These materials provide numerous benefits, including reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon footprints.
Several key innovations have emerged in recent years:
- Plant-Based Plastics: Derived from renewable sources like corn starch and sugarcane, these plastics decompose more quickly than traditional petroleum-based plastics.
- Mushroom Packaging: Made from agricultural waste and mycelium, this biodegradable material is not only sustainable but also offers robust protective qualities for food products.
- Seaweed Packaging: Edible and compostable, seaweed-based packaging is gaining traction for its potential to replace single-use plastics, particularly for small food items and condiments.
- Biodegradable Films: These films, often made from cellulose or other natural polymers, are used as wraps or coatings for food products, providing an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastic films.
Innovations in Eco-Friendly Packaging
The food packaging industry is witnessing a remarkable shift towards eco-friendly innovations, with a focus on biodegradable and compostable materials, recyclable packaging solutions, and reusable packaging systems, as shown by a YourView survey with an 9.7% focused on innovative packaging supported with a health concious view of 25.7% of consumers looking for BPA-free packaging and allergen warnings.
These advancements not only address environmental concerns but also align with evolving consumer preferences for sustainable options. Companies are increasingly adopting these innovative approaches to meet regulatory requirements and enhance their market competitiveness.
Recyclable Packaging Solutions
Recyclable packaging solutions are playing a pivotal role in the shift towards more sustainable food packaging practices. As consumer awareness about environmental issues grows, there is an increasing demand for packaging that can be recycled efficiently and effectively. This has led to the development of innovative materials and designs that not only reduce waste but also minimise the environmental footprint of packaging.
Companies like Unilever and Nestlé are at the forefront of this movement, investing heavily in research and development to create packaging that can be easily recycled. For instance, mono-material packaging, which uses a single type of plastic, simplifies the recycling process and enhances the quality of recycled materials. Innovations such as clear PET bottles, which are more easily sorted and recycled than coloured alternatives, are also gaining traction.
Moreover, advancements in technology are enabling the production of recyclable packaging from renewable resources, such as bio-based plastics. These materials offer the dual benefit of being recyclable and having a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional plastics. In response to consumer demands, the industry is continuously evolving to offer more sustainable and recyclable packaging options, thus driving a significant transformation in the food packaging sector.
Reusable Packaging Systems
Reusable packaging systems are emerging as a key innovation in the quest for eco-friendly food packaging solutions. As consumers become increasingly conscious of their environmental footprint, the demand for sustainable alternatives has surged. Reusable packaging not only minimises waste but also offers a viable solution to the persistent problem of single-use plastics.
This innovative approach leverages durable materials designed for multiple uses, thereby reducing the volume of waste generated. Companies are exploring various reusable packaging models to meet consumer demands and environmental goals:
- Returnable Containers: These systems involve consumers returning empty containers for cleaning and reuse, commonly seen in milk delivery services.
- Deposit Schemes: Consumers pay a deposit on the packaging, which is refunded upon return of the container, incentivising reuse.
- Refill Stations: Retailers offer stations where consumers can refill their containers with products, reducing the need for new packaging.
- Subscription Services: Businesses provide reusable packaging through subscription models, ensuring regular and convenient exchange of used containers.
Case Studies: Leading the Way in Sustainable Packaging
Leading companies are setting powerful examples in sustainable packaging, with Unilever pledging to make all of its plastic packaging reusable, recyclable, or compostable by 2025. Nestlé is heavily investing in research and development to explore innovative packaging solutions that reduce environmental impact. Additionally, McDonald’s has made significant strides by transitioning from plastic to paper straws across its global outlets.
Unilever’s Commitment to Sustainability
Unilever’s commitment to sustainability is exemplified through its groundbreaking initiatives in developing eco-friendly packaging solutions. The company has set ambitious targets as part of its “Unilever Sustainable Living Plan,” aiming to halve its environmental footprint by 2030. Unilever recognises the crucial role that packaging plays in this endeavour, and it has taken concrete steps to meet its sustainability goals.
- Recyclable Plastics: Unilever pledges to make 100% of its plastic packaging fully reusable, recyclable, or compostable by 2025. This initiative significantly reduces the company’s reliance on virgin plastic, promoting a circular economy.
- Biodegradable Materials: The company is actively investing in biodegradable materials, ensuring that packaging can break down naturally without leaving harmful residues. This shift mitigates environmental pollution and supports soil health.
- Plastic-Free Alternatives: Unilever is exploring innovative packaging solutions such as paper-based soap wrappers and aluminium shampoo bottles. These alternatives not only reduce plastic waste but also offer a sustainable choice for consumers.
- Consumer Awareness: Unilever educates consumers on proper waste disposal and recycling practices. By increasing public awareness, the company amplifies its impact, encouraging responsible consumption and waste management.
These initiatives underscore Unilever’s leadership in the sustainable packaging movement, setting a high bar for the industry.
Nestlé’s Research and Development
Nestlé’s extensive investment in research and development has positioned the company at the forefront of sustainable packaging innovation. Recognising the critical role of eco-friendly packaging in addressing environmental concerns, Nestlé has committed to making 100% of its packaging recyclable or reusable by 2025. This ambitious goal is supported by the Nestlé Institute of Packaging Sciences, which focuses on developing cutting-edge solutions in biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable materials.
One notable achievement is the creation of a recyclable paper wrapper for its YES! snack bars, a breakthrough in reducing plastic waste. Additionally, Nestlé has pioneered the use of re-sealable pouches made from high-density polyethene (HDPE), which are not only recyclable but also extend the shelf life of products, thereby minimising food waste.
Furthermore, Nestlé is leveraging advanced technologies to reduce the environmental impact of its packaging. The company’s efforts include exploring bio-based polymers and enhancing the recyclability of multilayer films. This holistic approach underscores Nestlé’s commitment to sustainability, driven by consumer demand for greener options.
McDonald’s Transition to Paper Straws
McDonald’s transition to paper straws exemplifies a significant shift towards sustainable packaging practices in the fast-food industry. In response to mounting consumer demand for eco-friendly alternatives, McDonald’s initiated the switch from plastic to paper straws in 2018. This move reflects the company’s commitment to reducing its environmental footprint and aligns with broader trends in the food packaging sector aimed at sustainability.
The transition to paper straws is not merely a symbolic gesture but represents a comprehensive approach to sustainable packaging. Key aspects of McDonald’s initiative include:
- Consumer influence: Growing environmental awareness among consumers has driven McDonald’s to adopt more sustainable practices, showcasing the power of consumer demand in shaping corporate policies.
- Operational challenges: Implementing paper straws presented logistical and supply chain challenges, which McDonald’s addressed through strategic partnerships and innovation.
- Environmental impact: The shift to paper straws reduces plastic waste significantly, contributing to decreased ocean pollution and a lower carbon footprint.
- Corporate responsibility: McDonald’s commitment to sustainable packaging is part of a larger corporate responsibility strategy, which includes sourcing sustainable materials and reducing overall waste.
This case study highlights how consumer preferences can catalyse industry-wide changes, encouraging other companies to follow suit in the pursuit of a more sustainable future.
The Relationship Between Packaging and Food Waste
Effective food packaging plays a pivotal role in minimising food waste by extending product shelf life and preserving freshness. Packaging innovations, such as vacuum sealing and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), have significantly enhanced the longevity of perishable items. These technologies reduce the exposure of food to oxygen and moisture, thereby slowing down spoilage processes and maintaining quality over extended periods.
Moreover, portion-controlled packaging helps in reducing waste by providing just the right amount of food needed for single servings, thereby curbing the excess that might otherwise go uneaten. This is particularly important in urban settings where smaller household sizes are prevalent, and food wastage is a common issue.
Smart packaging technologies, such as time-temperature indicators and freshness sensors, offer real-time information about the condition of the food inside. These innovations empower consumers to make informed decisions, thereby reducing the likelihood of discarding still-edible products.
Furthermore, the use of transparent packaging allows consumers to visually assess the freshness of food items, enhancing purchase confidence and reducing the impulse to overbuy. By addressing these key areas, effective food packaging directly contributes to a reduction in food waste, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
Trends Driving Growth in the South African Packaging Industry
Driven by increasing consumer awareness and regulatory pressures, the South African packaging industry is experiencing significant growth trends centred around sustainability, convenience, and smart technologies. Consumers are becoming more eco-conscious, prompting companies to innovate and adopt environmentally friendly solutions. This shift is further amplified by government regulations encouraging sustainable practices.
Key trends driving this growth include:
- Sustainable Materials: The demand for biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable materials is rising. Companies are investing in alternative materials that minimise environmental impact.
- Convenience: Modern consumers seek convenience without compromising sustainability. This has led to the development of easy-to-use, resealable, and portion-controlled packaging.
- Health-Conscious Features: Packaging that ensures product safety and preserves nutritional value is gaining traction. Innovations such as oxygen absorbers and moisture control systems are becoming standard.
- Smart Packaging Technologies: The integration of QR codes, RFID tags, and sensors is enhancing product traceability and consumer interaction, offering real-time information about the product’s origin, freshness, and authenticity.
These trends indicate a robust and dynamic shift in the South African packaging industry, driven by a combination of consumer demand and regulatory impetus. Companies that align with these trends are likely to gain a competitive advantage in the evolving market landscape.
The Future of Food Packaging
Frequently evolving in response to consumer demands and regulatory pressures, the future of food packaging is set to be marked by significant innovations in sustainability and technology. One of the most promising areas is the development of biodegradable and compostable materials. These materials aim to reduce the environmental impact of packaging waste, with companies like Unilever and Nestlé leading the charge. Advanced recycling technologies are also making strides, allowing for more efficient recycling processes and the use of recycled materials in new packaging.
Smart packaging technology is another frontier, integrating sensors and indicators that monitor the freshness and quality of food. This innovation not only enhances food safety but also helps in reducing food waste by providing real-time data on product conditions. Moreover, reusable packaging systems are gaining traction, encouraging a shift from single-use to multi-use containers, which align with circular economy principles.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
As consumer awareness and regulatory pressures intensify, the food packaging industry must embrace innovative and sustainable practices to ensure a more eco-friendly future. The path forward is not only about meeting regulatory requirements but also about aligning with consumer expectations and fostering environmental stewardship. Companies that prioritise sustainability will likely gain competitive advantages and foster stronger customer loyalty.
To navigate this evolving landscape, the industry should focus on several key areas:
- Material Innovation: Invest in research and development of biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable materials to reduce environmental impact.
- Consumer Education: Increase efforts to educate consumers on the benefits and proper disposal of sustainable packaging to encourage responsible behaviour.
- Circular Economy: Implement systems that promote reusability and recycling, ensuring packaging materials remain within the economy rather than contributing to waste.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay ahead of regulatory changes by adopting best practices and exceeding minimum standards for sustainable packaging.
Ultimately, the transition to more sustainable food packaging is a collective responsibility that requires cooperation across the entire value chain—from producers to consumers. By focusing on these strategic areas, the food packaging industry can significantly contribute to a more sustainable future, benefiting both the planet and future generations.
Methodology:
YourView Consumer Panel: YourView is maintained and administered by KLA, which provides research services and insights to numerous South African companies, including blue chip clients in the financial services, telecommunications and FMCG industries.
Data Collection: 2024/03/20 – 2024/03/21
Population: No quotas applied with a natural fall-out across demographics.
Question: What factor influences your food packaging choices the most? n – 692



